Request Appointment
Enter your details and we will be in touch with you shortly;
Or call
8655885566
between 8 am and 8 pm.
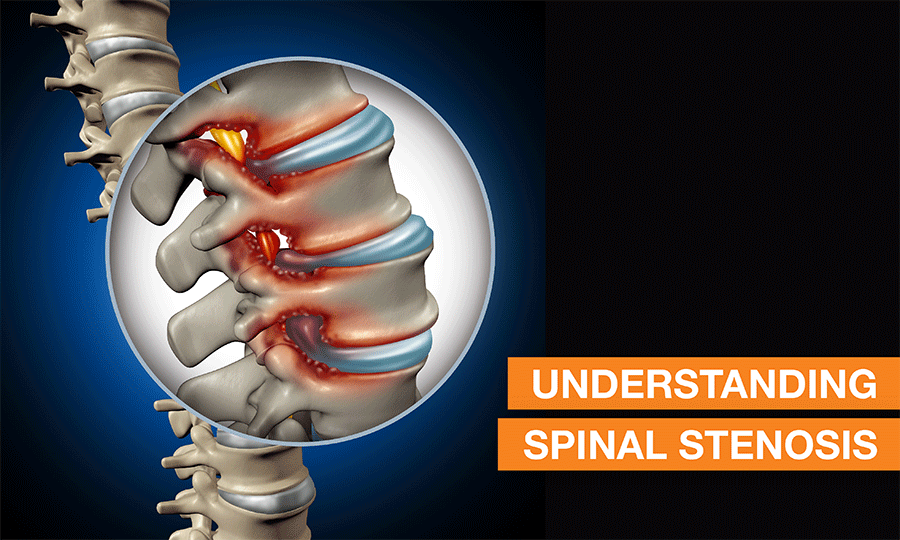
As we grow older, the body undergoes constant wear and tear that might leave you exposed to issues such as arthritis or herniated disc, etc. Back pain is considered a common musculoskeletal disorder estimated to affect 80% of the total human population during their lifetimes. Spinal stenosis is one of the back-related issues that you might face.
With the sensation of numbness in arms, loss of balance, etc, you might encounter spinal stenosis too. However, There’s no need to panic as there are both surgical and non-surgical treatment options available. Let’s have a look at what is spinal stenosis, the causes and symptoms, and what you can do about it non-invasively unless surgery becomes an absolute necessity.
The spine bone begins from the base of the skull to the tailbone and consists of 24 mobile vertebrae connected with discs in-between. The spine has three natural curves maintaining which, is considered a good posture. The spinal canal is the tube-like hollow space within the spine that holds a crucial set of long and tube-like band tissues called ‘Spinal Cord’ containing spinal nerves crucial for all our stimulus and reflexes.
Spinal Canal is a cavity between the posterior and anterior portions of the spine measuring about 14mm and above that holds the spinal cord. Spinal stenosis is a condition where the space in the canal gets narrowed due to ageing or other factors. It compresses the spinal cord and as the space gets narrower, you end up executing the symptoms ranging from weakness in arms or legs, loss of balance, numbness in legs, etc.
Spinal stenosis occurs gradually and at a slow pace. For instance, when you’re ageing. It is the reason why you might not show any symptoms even if the particular area of the spine is undergoing stenosis. X-rays, CT scans, MRI scans and other imaging tests are recommended by doctors to find the extent of the condition and the plan of action.
Based on where the spinal stenosis has happened, you might see different symptoms. Generally, it can result in symptoms such as loss of balance that elevates the risk of falling. Weakness in arms or legs or numbness in butts of legs is another set of symptoms. There’s also lower back pain when walking or standing that can be summed up as the symptoms. Loss of bowel or bladder control adds to the symptoms list as well.
Tandem spinal stenosis affects two regions of the spine and finally, there’s foraminal stenosis that can affect the part of the body where it branches out to. Usually, spinal stenosis affects one region of the spine but there are chances that you might have stenosis in two regions at once although it is not common.
Spinal stenosis can cause a series of problems, however, what actually contributes towards it? What are the causes of spinal stenosis? Let’s explore some of the causes to get a clear picture of this gradually developing back-related issue.
Herniated Discs:The spine is made up of movable vertebrates with cushioned disks in-between. These disks act as shock absorbers. A herniated disc may happen if the outer layer of the disk ruptures letting the nucleus ooze out pressing on the nerves.
Bone Spurs:Constant wear and tear occurs when you age. It can lead to the development of extra bone known as bone spurs. It can press on the spinal nerves leading to situations such as spinal stenosis.
Spinal Injuries:Bone fractures, car accidents, or other trauma can cause spinal bones to break and displace. It can cause swelling and may end up compressing the spinal cord.
Tumors:Unwanted tissue growth in the spinal canal may take up space in the spinal canal compressing the foramen for the spinal cord as a result.
Thick Ligaments:The ligaments that join bones in your spine may become stiff and thickened consuming more space in an already compact spinal canal.
Medications can help treat spinal stenosis non-invasively based on the severity of the condition. Analgesics are medications that help with pain relief on a temporary basis. Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) are the ones that reduce inflammation associated with spinal stenosis and help with pain relief. There are steroids, anti-seizure drugs, opioids, and anti-depressants that your doctor should be able to prescribe after analysing your current and past medical records.
We often neglect the fact that exercises are good for our health. With proper physical therapy supervised by a healthcare professional, it can work wonders. You will learn the correct posture as well as techniques to take away the stress on the back and strengthen the core gradually.
Making some corrective changes in our daily routine makes a lot of difference. For instance, correcting the posture when sitting on a chair takes away the excessive stress your spine has to endure. Creating a supportive workstation where your back gets ample support will help you in the long run.
Spinal stenosis grows gradually and may take years before showing any symptoms. Taking precautionary measures such as physical therapy and medications can prevent the condition from deteriorating. Reach out to QI Spine Clinic at 086558 85566, India’s first non-invasive spine rehabilitation clinic that helps you fix all spine-related issues.
Visit our nearest clinic for your first consultation